In the dynamic research landscape, leaders, scientists, and scholars must have dependable ways to discover relevant studies and evaluate their impact.
Traditional methods, while foundational, often struggle to keep pace with the sheer volume of publications generated each year. As technology continues to develop and evolve, AI promises a truly modernized approach to the discoverability and evaluation of research.
By leveraging machine learning algorithms and natural language processing, AI can transform these critical processes, making it easier for researchers to find information quickly and accurately. This shift accelerates scientific progress and democratizes access to knowledge, potentially leading to groundbreaking advancements across diverse fields.
Extracting Needles From Haystacks
Smart Citations serve as the fundamental element of scite. These sophisticated citations consist of text excerpts extracted from the citing article's full text, which are then categorized as either providing supporting evidence or analysis for the citation or contrasting evidence or analysis.
But precisely how do we extract this information? How do you analyze millions of PDFs to get these citation statements?
This is where machine learning comes in.

We use nearly a dozen machine learning models to reliably identify in-text citations and match those citations to the correct reference in the reference section. We then need to take that string of information and match it against metadata identifying the article. We have made significant progress refining this process, enabling us to extract this information consistently and at high volumes. And this doesn't just apply to more recent research. We can go back to PDF versions of records even hundreds of years old (Robert Hooke’s 1665 piece on Micrographia, anyone?)
Yay, Or Nay?
Once we have this in-text citation, we extract not only the sentence where the citation happens but also the sentence before and after it. We then classify the citation sentence using a deep learning model, determining if there is supporting evidence in the citation statement or contrasting evidence in the citation statement.
This method was developed by reading approximately 40,000 citation statements, looking solely at context. We annotated each to note if the authors cited it in support (indicating evidence or analysis behind the claim) or if they were challenging it. This fed the deep learning model, which allows us to classify citation statements at scale.
Because we're talking about a billion of these, right? It's just too much for humans to tackle.
Therefore, we're using AI to solve these specific problems, not to be fancy or jump on the AI bandwagon, but because it's necessary to process the sheer volume of available information.
We're All In This Together
The goal of developing these next-generation citations is not to operate a small group acting independently but to cooperate with other tool providers and publishers to make this information as accessible as possible.
We've made good progress working with publishers to display our citations on the version of record, evolving from "Here's an interesting idea" to "Here's what the future citations will be."
Now we're live on millions of articles across Wiley, the Royal Society, the American Physiological Society, PNAS, Wolters Kluwer, American Chemical Society, and many more.
This has begun influencing and impacting research across disciplines, improving how researchers understand, evaluate, and identify competing evidence against the literature.
ChatGPT Takes The Stage
Meanwhile, as we work towards our mission to better organize the world's knowledge and better understand scholarly information, in comes ChatGPT.
ChatGPT has taken the world by storm, impacting essentially everyone's role or work in some way, shape, or form. And research is no exception.
ChatGPT is exceedingly powerful, easy to use, and flexible; however, it comes with its own host of challenges.
Researchers may ask questions of ChatGPT to determine if it's something they can use to help with writing or to help with understanding articles. And it can produce impressive outputs that look quite confident, even if they are made up.

This results in understandable concerns: you hesitate to use ChatGPT where there may be life or death consequences or where substantial grant money or investments are involved. No one has the time to go through and check whether all responses are valid; results need to be trustworthy for this to be a viable solution.
How can we utilize the amazing capabilities of Large Language Models and ChatGPT to build trust and save time to leverage for research properly?
ChatGPT Needs Citations
Developing the next generation of citations to help assess and discover scholarly literature, working alongside the behemoth that is ChatGPT, we are well positioned to fact-check and source Large Language Model output against the vast, unique pool of peer-reviewed scientific literature and that "single source of universal truth."
Therefore, we present scite Assistant - ChatGPT for Science.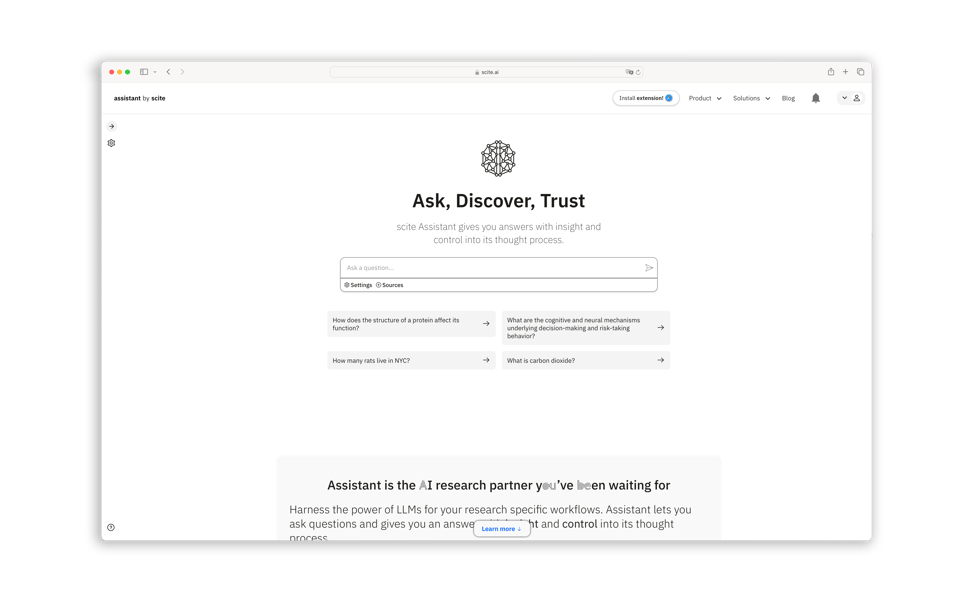 scite Assistant allows researchers to ask any question or to give any prompt they want, with all the flexibility of ChatGPT, but running on scholarly articles. This means researchers are provided with validated outputs that can be trusted, quickly understanding if the reference is correct or has been challenged.
scite Assistant allows researchers to ask any question or to give any prompt they want, with all the flexibility of ChatGPT, but running on scholarly articles. This means researchers are provided with validated outputs that can be trusted, quickly understanding if the reference is correct or has been challenged.
Researchers can use this to get drafts done quickly, to understand a given discipline or field better, and to help develop search strategies for research search engines.
Catalyzing Trust in Research: Empower Your Work with Research Solutions
Where today’s flood of information challenges the trustworthiness and efficacy of research, researchers need tools that simplify knowledge acquisition while enhancing the reliability of scholarly content.
scite Assistant, part of Research Solutions’ product family, represents a pioneering leap in this endeavor. By seamlessly integrating AI with our practical approach to assessing the impact and credibility of scholarly work, we equip users with a powerful resource to navigate the complexities of academic literature with confidence.
Book a demo today to learn how our solutions can transform your engagement with academic literature, empowering you to contribute to advancing knowledge with certainty and reliability. Or, to gain further insights into leveraging Generative AI responsibly in research, watch our two-part webinar on effectively utilize AI while maintaining high standards of credibility: ChatGPT for Science.
1 Nicholson, J. M., Mordaunt, M., Lopez, P., Uppala, A., Rosati, D., Rodrigues, N. P., … & Rife, S. C. (2021). Scite: a smart citation index that displays the context of citations and classifies their intent using deep learning.. https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.03.15.435418
.png?width=970&height=571&name=New%20Blog%20Header%20Graphic2%20(1).png)
.png?width=970&height=571&name=New%20Blog%20Header%20Graphic2%20(2).png)